Image Masking in Photoshop is a non-destructive background removal technique that allows editors to precisely separate image subjects—especially those with soft or complex edges—by using layer masks instead of deleting pixels.
What is Image Masking in Photoshop?

Image masking focuses on isolating the main subject from its background by controlling visibility rather than removing pixels. The technique adapts to different subjects and edge types, including hard edges, soft edges, and semi-transparent areas.
Unlike other background removal methods that are limited to specific use cases, image masking works effectively across a wide range of images. Because the original pixels remain intact, editors can refine, adjust, or reverse selections at any stage, making image masking a flexible and professional editing method.
Why Do You Need Image Masking in Photoshop?
Image masking is essential in professional photo editing because it allows precise background removal without damaging the original image. This non-destructive technique gives editors full control over complex edges and enables flexible editing at any stage of the workflow.
Unlike basic background removal methods, image masking remains effective when dealing with challenging subjects such as hair, fur, shadows, or semi-transparent objects. For this reason, it is widely used in advanced Photoshop editing.
Key Reasons to Use Image Masking
- Remove or replace backgrounds without permanently deleting pixels
- Maintain full control through non-destructive editing
- Cut, modify, or refine specific areas with minimal effort
- Show or hide image areas easily using brush tools
- Create creative effects such as text masking and clipping masks
- Build photo collages while keeping the option to revise changes anytime
Types of Image Masking in Photoshop
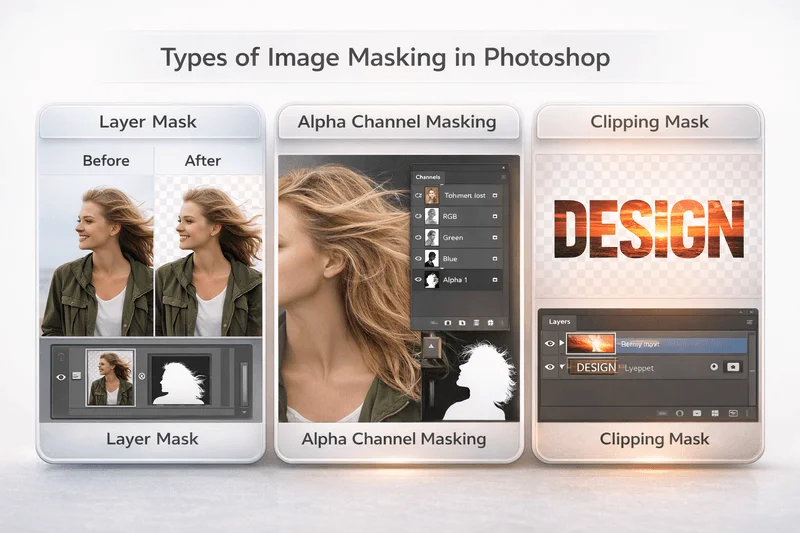
Image masking in Photoshop can be applied in different ways depending on the subject, background complexity, and editing purpose. Each type of image masking serves a specific function and is used in different editing scenarios. Below are the most commonly used types of image masking in Photoshop.
1. Layer Mask
Layer masking is the most widely used type of image masking in Photoshop. It allows editors to hide or reveal parts of an image without deleting any pixels. Using black and white brush strokes, you can control which areas remain visible and which areas are hidden.
Layer masks are ideal for:
- Non-destructive background removal
- Refining edges like hair or soft objects
- Making reversible edits at any stage
2. Alpha Channel Masking
Alpha channel masking is used when dealing with highly complex edges, such as hair, fur, smoke, or transparent objects. This method stores selection information in a separate channel, allowing for extremely precise masking.
Alpha channel masking is commonly used for:
- Complex product images
- Portraits with fine hair details
- Professional-level photo compositing
3. Clipping Mask
Clipping masks are used to control the visibility of one layer based on the shape of another layer. This type of masking is especially popular for creative designs rather than background removal.
Clipping masks are commonly used for:
- Text masking effects
- Applying images inside shapes or text
- Creative typography and graphic design layouts
How Image Masking Works?
Image masking in Photoshop follows a simple three-step workflow that helps editors isolate subjects accurately while keeping the editing process non-destructive. Each step plays a crucial role in achieving clean and professional results.
Step 1: Selection
The first step in image masking is creating an accurate selection of the subject. Photoshop offers several selection tools, such as the Quick Selection Tool, Pen Tool, and the Select Subject option. The choice of tool depends on the subject’s shape and edge complexity.
For subjects with soft or detailed edges like hair or fur, using the Select and Mask workspace provides better control and precision.

In the photograph, we have a soccer ball on a field. We have selected the ball with the quick selection tool. You can do it by simply clicking the ‘Quick Selection Tool’ from the Tools panel. Then click and move over the subject area until you select the whole area.
You can increase or decrease the brush size by pressing the keyboard keys “]” and “[“. Also, you can do this, press and hold Alt/Option for Win/MAC and click the right mouse button & move right or left. Each procedure does the same thing, only in different ways.
Step 2: Mask Addition
a. Vector Mask

When you are satisfied with the selection, it is time to add the mask. Adobe Photoshop has two ways to add a Layer Mask. Click on the ‘Add a vector mask’, located at the bottom of the Layers panel. Clicking this, you will have the mask according to the selection.
b. Select and Mask After Making a Selection

Another way of adding a mask is to right-click on the selected area and left-click on the ‘Select & Mask’ option. A new window will open where you can edit and modify even more. Also, you will see some more options to polish the edges with Photoshop’s artificial intelligence.
In the output settings, you will have options to choose how you want the selected area. In general, you need to choose ‘Layer Mask’ and press OK to continue.
c. Select & Mask Before Making a Selection

You can follow the second option directly. Just use the ‘Select & Mask’ option when you are using a selection tool. As soon as you click on that button, you will have your image in a new window. Then, make the necessary changes and save the selection as a ‘Layer Mask’.
By the way, if you go through this, you can also use the ‘Select Subject’ option. Photoshop will do some calculations and select the subject by artificial intelligence. And you can modify the selection here as well.

If you have an image with a subject that is not super complex, Photoshop can do the selection better than you can imagine. The example is as below. Here, the subject (Football) is clear to look at, which is selected. And the area around the ball is like an onion skin, which is not selected.
Step 3: Apply Layer Mask

Once the masking is complete, apply the layer mask to continue editing smoothly. Right-click on the mask and select the ‘Apply Layer Mask’ option.
Now, you will have the subject only and do whatever you want to. You can add another background or use a solid color instead. Also, you can add a Drop Shadow or any shadow you want. For product photographs, we use the Drop Shadow the most.
Step 4: Save
After completing all edits, save the file in a format that suits your needs. For future flexibility, it is best to save the image in PSD format first, as it preserves layers and allows further adjustments later. Once finalized, the image can be exported in other formats such as JPEG, PNG, or TIFF.
Image Masking vs Clipping Path
Image masking and clipping path are both widely used background removal techniques, but they are suitable for different types of images. While clipping paths work best for subjects with hard and well-defined edges, image masking is more effective for complex images with soft or intricate edges.
To explore the key differences, use cases, and real-world examples in detail, read our complete guide on Image Masking vs Clipping Path.
Common Uses of Image Masking
Image masking is widely used in professional photo editing across various industries, including eCommerce, advertising, and graphic design. It helps editors achieve clean cutouts, realistic composites, and visually appealing compositions.
For a complete breakdown of real-world applications, practical examples, and industry-specific use cases, explore our detailed guide on Common Uses of Image Masking.
Conclusion
Image masking in Photoshop helps separate subjects from backgrounds without damaging the image. It works well for complex details like hair or transparent objects and allows easy editing at any time. This technique improves image quality and makes edits look more realistic.
If you need professional image masking services with precise edge handling and non-destructive editing, Clipping World offers reliable solutions for eCommerce, advertising, and creative projects. Learn more about our image masking services to get clean and accurate results for even the most complex images.
FAQ | Image Masking in Photoshop
Image masking in Photoshop means using a layer mask to hide or reveal parts of an image without deleting pixels. This allows non-destructive editing and greater control over complex edges. For more technical details, you can also refer to Adobe’s official Photoshop documentation.
The main purpose of image masking is to isolate subjects from their backgrounds accurately while keeping the original image intact. It is especially useful for images with soft, detailed, or transparent edges.
Yes, image masking is a non-destructive technique because it does not permanently remove any pixels. Editors can modify or reverse changes at any time.
Image masking should be used when working with complex subjects, transparent objects, or when precise edge control is required for professional-quality photo editing.

